Difference between revisions of "Wiki Syntax"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (10 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | This page is about the Wiki source code syntax. There are also Information on [[How-to-Contribute]]. | |
| + | == Pictures == | ||
| + | # Make sure you know or have the licenses to the uploaded material and only use it accordingly!! | ||
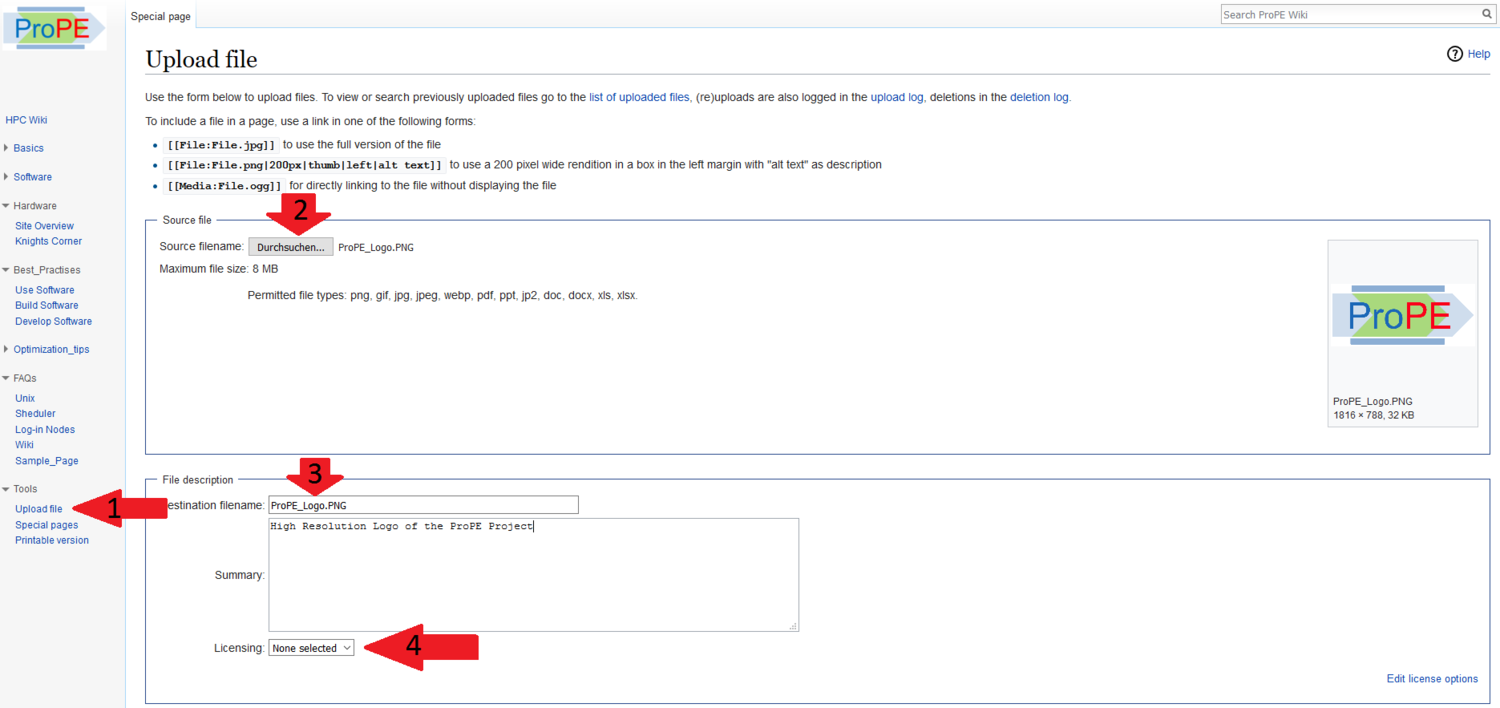
| + | # Upload the picture to the Wiki: [[File:Upload_Picture.PNG|center|1500px]] | ||
| + | # Link the File into the article with <source>[[File:ProPE_Logo.png|1000px]]</source> | ||
| + | # [https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Help:Images Format] the picture how you like it :) | ||
| + | |||
| + | == <span id="UsingIDs"></span> Heading IDs == | ||
| + | |||
| + | When creating internal links to sections, use the id of the heading rather than the current heading name. One advantage of these types of references is, that you are not relying on the plain text of the heading, but rather an internal id. Unlike the id, the heading might change during the development of this Wiki and as a result all links to this heading will break. To create an heading with id <code>UsingIDs</code> for this section: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 85%;" | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Invisible span element in front of the visible heading text<br> | ||
| + | [[#UsingIDs|internal link to id UsingIDs]]<br> | ||
| + | [[#Heading_IDs|internal link to heading Heading_IDs]] | ||
| + | | | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | == <span id="UsingIDs"></span> Heading IDs == | ||
| + | [[#UsingIDs|internal link to id UsingIDs]] | ||
| + | [[#Heading_IDs|internal link to heading Heading_IDs]] | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == LaTeX Formula == | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 85%;" | ||
| + | | <math> a+b = c</math> || <<nowiki />math> a+b = c<<nowiki />/math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Code Segmente mit Syntax Highlighting == | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 85%;" | ||
| + | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
user1@blablubb:~/test$ ls datei* | user1@blablubb:~/test$ ls datei* | ||
datei datei1 datei2 datei3 datei4 datei5 datei6 # Auch 'datei' ohne Nummer | datei datei1 datei2 datei3 datei4 datei5 datei6 # Auch 'datei' ohne Nummer | ||
| Line 8: | Line 41: | ||
user1@blablubb:~/test$ ls datei[1-3] # Wertebereich | user1@blablubb:~/test$ ls datei[1-3] # Wertebereich | ||
datei1 datei2 datei3 | datei1 datei2 datei3 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | | <source> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | user1@blablubb:~/test$ ls datei* | ||
| + | datei datei1 datei2 datei3 datei4 datei5 datei6 # Auch 'datei' ohne Nummer | ||
| + | user1@blablubb:~/test$ ls datei? | ||
| + | datei1 datei2 datei3 datei4 datei5 datei6 | ||
| + | user1@blablubb:~/test$ ls datei[1-3] # Wertebereich | ||
| + | datei1 datei2 datei3 | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="python"> | + | | <syntaxhighlight lang="python"> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
import numpy as np | import numpy as np | ||
| Line 28: | Line 64: | ||
# ----- Switches -------------------------------------------------------- | # ----- Switches -------------------------------------------------------- | ||
debug=False | debug=False | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
call_gnuplot=False ## call gnuplot automatically generates gnuplot | call_gnuplot=False ## call gnuplot automatically generates gnuplot | ||
| − | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | | <source> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="python"> | ||
| + | import numpy as np | ||
| − | + | def main(): | |
| − | + | # ======================================================================== | |
| − | + | # Initialisation | |
| − | + | # ----- Switches -------------------------------------------------------- | |
| − | < | + | debug=False |
| + | call_gnuplot=False ## call gnuplot automatically generates gnuplot | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |} | ||
Revision as of 09:49, 30 April 2019
This page is about the Wiki source code syntax. There are also Information on How-to-Contribute.
Pictures
- Make sure you know or have the licenses to the uploaded material and only use it accordingly!!
- Upload the picture to the Wiki:
- Link the File into the article with
[[File:ProPE_Logo.png|1000px]]
- Format the picture how you like it :)
Heading IDs
When creating internal links to sections, use the id of the heading rather than the current heading name. One advantage of these types of references is, that you are not relying on the plain text of the heading, but rather an internal id. Unlike the id, the heading might change during the development of this Wiki and as a result all links to this heading will break. To create an heading with id UsingIDs for this section:
|
Invisible span element in front of the visible heading text |
== <span id="UsingIDs"></span> Heading IDs ==
[[#UsingIDs|internal link to id UsingIDs]]
[[#Heading_IDs|internal link to heading Heading_IDs]]
|
LaTeX Formula
| <math> a+b = c</math> |
Code Segmente mit Syntax Highlighting
user1@blablubb:~/test$ ls datei*
datei datei1 datei2 datei3 datei4 datei5 datei6 # Auch 'datei' ohne Nummer
user1@blablubb:~/test$ ls datei?
datei1 datei2 datei3 datei4 datei5 datei6
user1@blablubb:~/test$ ls datei[1-3] # Wertebereich
datei1 datei2 datei3
|
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
user1@blablubb:~/test$ ls datei*
datei datei1 datei2 datei3 datei4 datei5 datei6 # Auch 'datei' ohne Nummer
user1@blablubb:~/test$ ls datei?
datei1 datei2 datei3 datei4 datei5 datei6
user1@blablubb:~/test$ ls datei[1-3] # Wertebereich
datei1 datei2 datei3
</syntaxhighlight> |
import numpy as np
def main():
# ========================================================================
# Initialisation
# ----- Switches --------------------------------------------------------
debug=False
call_gnuplot=False ## call gnuplot automatically generates gnuplot
|
<syntaxhighlight lang="python">
import numpy as np
def main():
# ========================================================================
# Initialisation
# ----- Switches --------------------------------------------------------
debug=False
call_gnuplot=False ## call gnuplot automatically generates gnuplot
</syntaxhighlight> |